Parents often wonder what the normal heart rate for a child is. Well, in this digital era, it’s easy to find such information.
Checking and monitoring your child’s heart rate can save you countless worries. After all, we’re talking about the organ that literally pumps us through life.
In this article, we’ll discuss the normal heart rate for a child and how it changes with age and growth.
The Basics of Heart Rate
Firstly, we need to understand what a heart rate is. A heart rate represents the speed at which your heart beats.

Our heart beats at a normal pace while sitting or laying in our comfortable beds. But when we’re exercising, or are under stress, our heart beats faster.
Studies have shown that the human heart doesn’t beat as fast when exercising as the person ages.
Also, a person’s heart rate can indicate many illnesses. So, that’s why parents must track their children’s heart rates.
Normal Range of Heart Rate for Children (Chart)
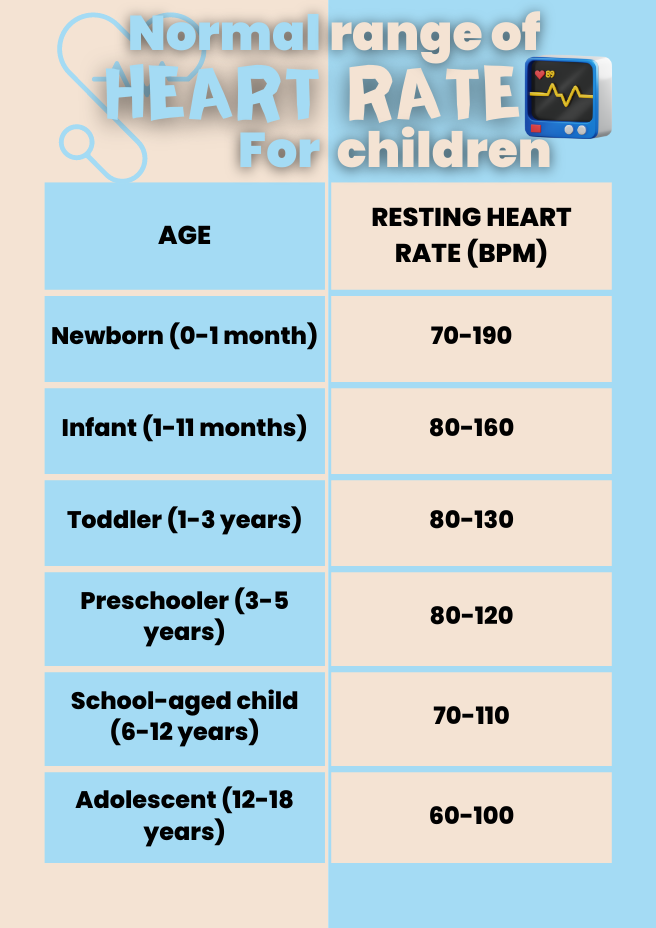
In the following paragraphs, we’ll discuss the normal heart rate for a child across different age groups.
· Newborns and Infants (0 – 12 months)
A normal resting heart rate for newborns and infants is 70-190 BPM (beats per minute). This heart rate may vary due to different factors, including:
- Illnesses;
- Stress;
- Excitement;
- Metabolism;
It’s very important to let medical experts monitor your children’s heart rate at this age since it can be a sign of dangerous heart disease.

· Toddlers and Preschoolers (1 – 5 years)
The normal heart rate for toddlers and preschoolers is 80-130 BPM. But these numbers can also vary. At this age, children learn to walk, run, and jump, so they spend plenty of time doing physical activities.
That’s why their heart rate may rise when they run, play, or jump around. But you must them to a medical expert if you notice their heart beats fast too often.
· School-Aged Children (6 – 12 years)
The normal heart rate for school-aged children is 70-110 BPM. At this age, children must stay active and often be outdoors.
Modern children often pick up their phones and tablets at this age. So, it’s crucial to limit screen time and promote healthy habits.
The American Academy of Pediatrics advises that children shouldn’t use tech for more than 2 hours daily.
· Adolescents (13 – 18 years)
And now it’s time for the teenagers. The normal heart rate for adolescents is 60-100 BPM. Teenagers’ heart rate may be affected by hormonal changes and physical activities.
We all know how hard it can be with teens but it’s still important to promote healthy habits and outdoor activities.
How to Measure Heart Rate in Children
Did you know you can measure your children’s heart rate at home? Who needs doctors?! (please don’t take that seriously!)
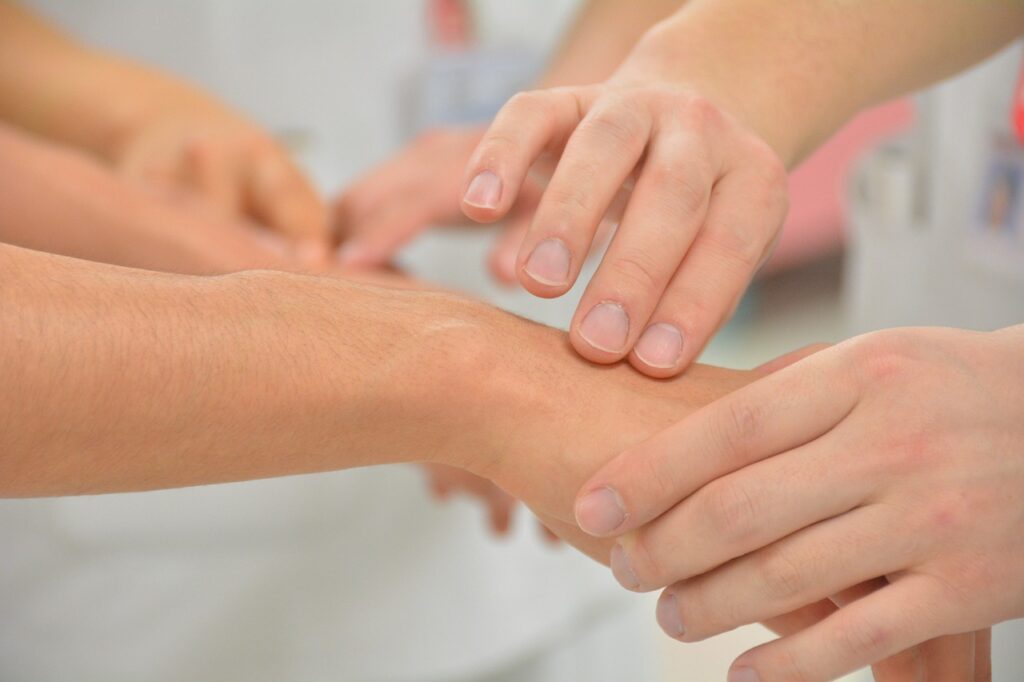

Just follow this step-by-step instruction, and you’ll have your child’s heart rate in just 10 seconds:
- Gently place two fingers below your child’s palm;
- Find a pulse and gently press your fingers on that spot;
- Measure the beats for 10 seconds;
- Multiply the number of beats by 6, so you can get the number of beats per minute;
And that’s about it! If you notice abnormal heart rates, even when your child is resting, contact medical experts!
Recognizing Abnormal Heart Rates
So, you’ve learned what the normal heart rate is for a child and how to measure it. Now, you should learn to recognize abnormal heart rates.
If you notice that your child has a slower heart rate than the usual one, that means your child has bradycardia.
However, if your child’s heart beats faster than normal, it means that your child has tachycardia.
Frequent tachycardia and bradycardia can point to heart disease in your children. So, if you notice abnormal heart rates, contact a doctor.

But you also shouldn’t freak out when your child’s heart beats faster when running or playing. That’s normal. Even the adult heart beats fast when exercising.
Factors Influencing Heart Rate
Many factors influence the heart rate in children. We’ll quickly address these factors in the following part of the article.
· Physical Activity and Exercise
Our heart beats fast when we do physical activities and exercise. But why is that? Our body needs more oxygen when we exercise, which is transported with red blood cells.
So, our heart pumps faster to supply our body with enough blood to have the required oxygen intake.
· Body Temperature and Hydration Levels
When we have a high body temperature, we sweat, so more blood is required in our skin. That’s why our heart beats faster (our heart rate is higher) when we have a fever.
Hydration levels also affect heart rate. If you’re dehydrated, your heart will beat faster and pump more blood.
· Emotional and Psychological Factors
Increased stress can also lead to tachycardia (higher heart rate), which can later result in more dangerous heart diseases.

Studies also support the claim that emotional and psychological trauma can cause lead to heart problems. So, one less worry a day keeps the cardiologist away!
Importance of Monitoring Heart Rate
Monitoring your children’s heart rate is crucial because it can be a way to discover dangerous illnesses early on.
Early discovery will give medical experts more time to think about the problem and treat your child. You must also monitor your children’s heart rate if they regularly play sports or exercise.
If you notice any abnormalities, contact a doctor as soon as you can. After all, our children’s health is most important to us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What heart rate is too high for a child?
It depends on the age. For infants and toddlers, a heart rate of 200 BPM is too high, while for older children, heart rates above 130 BPM are considered high.
What is normal resting heart rate for a newborn?
The normal resting heart for a newborn is 70-190 BPM.
Can emotional stress impact a child’s heart rate?
Yes, stress can increase a child’s heart rate.
What roles does genetics play in determining heart rate?
Inherited genetic mutations can often cause abnormal heart rhythms.
Does a child’s heart beat faster when sick?
Yes, a high fever can lead to a higher heart rate.
ALSO READ: Can I Predict My Baby’s Eye Color?







